As part of the City of Tulsa’s ongoing mission to provide residents the highest quality water and service, more than 145,000 residential water meters will be upgraded over the next several years with new automated water meters.
The replacement of City water metering equipment is part of the AMR/Service Line Inventory Program, a joint program that also will involve a systematic investigation to categorize service line material and ensure our system is free of lead pipes.
The meter installation program is expected to begin in fall 2023 and is estimated to take 3-4 years to complete.
The new automated water meters will provide Tulsa water customers numerous benefits, including:
Learn more about the True Reads automated meter replacement program.
A majority of the City’s current water metering equipment works like a car odometer that measures a customer’s water usage. City employees manually read the meters each billing cycle.
Automated Meter Reading (AMR) is a communication technology used by water utilities to automatically collect water consumption data from water meters.
Once installed city-wide, the new AMR meters will automatically store water usage data that can be transmitted to a City vehicle driving down the street using a low-level radio signal (similar to signals currently used in City trash carts or in PikePass sensors).
The meter data is then transferred to a database, where the City’s Utility Billing Department can monitor and analyze usage, troubleshoot issues and bill customers based on actual consumption instead of estimates.
In addition to providing more accurate data, the automated meters will create a safer work environment for City work crews – since the meter data will be collected remotely with AMR technology, City employees will not need to walk through neighborhoods to manually read meters.
In 2022, a new federally mandated regulation – the revised Lead & Copper Rule (LCRR) – was announced by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) requiring all U.S. cities to develop and update their inventory of lead service lines by October 16, 2024.
Tulsa is complying with this EPA mandate by capitalizing on the installation of the new AMR meters to conduct an extensive investigation of service lines in the city (where lead lines or connectors would be located).
“We’re pairing these two projects together to save money and be as efficient as possible to meet these requirements and provide the highest quality water to our customers,” said City Water Director Eric Lee.
According to Lee, the City of Tulsa does not have lead water mains and historical records show copper and galvanized metal pipe were used for service lines in Tulsa in the past. However, during previous inspections Water & Sewer Staff have found a small amount of lead connectors (small sections of pipe used to connect a house’s service lines to meters or a mainline).
“The City has been replacing these lead connectors since the 1950s as we’ve found them during routine work on water lines and meters,” Lee explained. “We typically see these lead connectors in older parts of town where the construction dates from the 1920s and 1930s.”
He said City crews have done initial inspections of 600-700 homes of the oldest construction date; in those houses, less than 1 percent had lead connectors and none had longer lead service water lines.
The City is currently taking bids from contractors to perform the meter replacement work, with work scheduled to begin in early 2023.
Why is the City of Tulsa installing new water meters?
The City has had a reliable process for reading and changing out meters for many years. But AMR technology has improved to the point that it now makes financial and operational sense to switch to AMR to ensure meter reading accuracy and consistency for customers.
What are the benefits of AMR?
How does AMR work?
Using wireless radio transmitters, AMR remotely reads your meter and then transfers the data into a billing system. AMR will drastically reduce the need for meter readers to manually gather utility meter readings.
Will City employees still need to manually read my meter?
Once the new AMR meter is installed, your meter data will be collected remotely without City workers manually reading the meter.
Will City employees lose their jobs due to this automated process?
No, no employees will lose their jobs with the updated meter reading process.
When will the meter installations begin?
Installation of Tulsa’s AMR water meters started in spring, 2023.
Who is performing the work?
ENVOCORE RTS Water Solutions is performing the work. These City contractors will be in marked vehicles, with ID badges and uniforms.
How long will it take to complete the meter installation project?
The AMR meter installation project is estimated to take 3-4 years to complete.
Do I need to pay to have my meter installed?
The City of Tulsa is paying to purchase and install the meter to improve service to its water customers.
How will I know when my new water meter is scheduled to be installed?
Is my water meter on the outside of the home?
Residential water meters are located outside the home, typically near the curb in a round metal meter can.
Will workers need to enter my home in order to install the new meter?
No.
How many AMR water meters will be installed by the City?
The City of Tulsa will be installing approximately 145,000 new AMR meters.
How long will it take for my meter to be installed?
Once inside your yard, each meter installation will take approximately 20-30 minutes.
Do I need to be home for this AMR meter installation?
No, you do not need to be present for crews to switch out your meter.
Are the new AMR water meters larger than the old meters?
The new AMR meters will be the same size as your current meter.
Will the City crews need to interrupt my water service to switch out the meter?
Service interruptions will generally last less than 30 minutes.
Are these new AMR water meters more accurate than the current water meters?
The City’s current water meters need to be read manually, and sometimes mistakes can happen when entering the information. Also, as the current water meters age they tend to under-register and are not as accurate. The new AMR meters do not under-register as they age and have an expected life range twice as long as the current meter.
Are the new AMR meters more durable than current meters?
The new AMR meters use ultrasonic metering technology, which means they have no moving parts that require maintenance. The meters have a life expectancy of 20 years, which is twice as long as the current meters.
Tulsa will begin placing meters in plastic high-density polyethylene meter boxes instead of galvanized meter cans, which rust easily. The plastic boxes can potentially last 50 years.
The rectangular design of the new meter box could also mean less injuries to City employees.
What information are you capturing with this AMR technology?
The equipment collects and transmits water usage information and the meter identification number. Diagnostic information is also transmitted to verify that the meter is operating correctly.
Is my account information secure?
Yes, only meter readings and meter numbers are transmitted. Personal customer information will not be transmitted.
Is this new AMR system really needed?
The City of Tulsa strives to provide the best possible customer service, high reliability and billing accuracy. The AMR technology will help us achieve these goals by improving efficiency and accuracy.
Are there any potential health concerns with the radio signals?
Numerous studies made on low-power radio frequency transmissions have revealed no negative health impacts.
Where is AMR technology utilized in Tulsa?
Other Tulsa utilities PSO and ONG already utilize this automated meter technology, and nearby communities like Jenks and Owasso use AMR for their water systems. In addition, the City of Tulsa has been using AMR meters for years in areas where it is difficult or dangerous to manually read meters.
Will the radio signals interfere with other equipment in my house?
The radio transmissions last less than one second and occur on a frequency different from those used by television signals, cordless phones, garage doors and pacemakers. Also, AMR meters are located outside the home, typically near the curb.
What powers the AMR radio transmitter?
The radio is a battery-powered device with an expected battery life of 20 years.
How will you know that my reading is accurate?
The meters exceed American Water Works Association C715 accuracy standards, and the manufacturer warrants the accuracy levels for the life of the meters. Each meter shipment is accompanied by factory test data showing the accuracy of the meter as tested at the factory.
This “state-of-the-art” meter reading technology uses electronic registers to collect the meter readings and a radio to send the data. It has proven to be more accurate than visually reading the meter by removing the possibility for human errors.
Also, each radio device has a unique identification number that is transmitted along with the meter reading. The unique identification number is compared electronically to your account record to ensure that the meter reading received matches the meter assigned to your account.
Does this mean my water bill will be increasing?
Not necessarily. In some cases, your bill could increase but only if your current meter is under-reporting your usage.
Will this help me save money on my water bill?
The new AMR meter will more accurately measure your water consumption so you are paying only for the water that you use.
Will my water bills be higher to pay for this new technology?
Your water bill will better reflect your actual water consumption with this new AMR technology and do away with estimated water bills, so your bill will be higher or lower based solely on your water consumption.
The cost of the new AMR technology is being paid for as part of the Tulsa Water & Sewer Department’s multi-year budgeting for this technology.
Will you have to dig up my yard to switch out the new water meters?
When the contractor crew installs your meter they may need to dig near your meter can, but they will restore your yard to as close to its original condition as possible. Following the meter can replacement, the City’s contractor, Envocore/RTS Solutions, will complete soil restoration for any greenspace locations where a disturbance occurs. Meter cans located in sidewalks and driveways will require paving cuts to replace. The City of Tulsa will complete restoration in these areas. In the program’s first week, rainy and wet conditions hindered the initial soil restoration process that our contractors have since gone back in and addressed. Should any future soil disturbances occur that are not addressed within 7 days as part of the True Reads project, residents are encouraged to report them to 311.
Will the new AMR meter cause problems with my regular lawn maintenance?
The new AMR meter box and lid will be easily secured by the City and be as flush with the graded ground as possible. It will not disrupt resident mowing or be a trip hazard.
NEW: My new meter can is installed at an angle. Why?
This is because your service line runs at an angle from the mainline to your home. With the round cans this was not noticeable, but with the square cans it will be more noticeable.
Will I see a change in my service after AMR is installed?
The only significant change to your utility service will be that once the AMR meter is installed and operating, meter readers will not need to visit your property to collect the meter readings.
Will I need to do anything to maintain the AMR meter?
City personnel may visit the meter periodically to confirm proper operation or perform routine maintenance.
Is this something I have to do?
Yes, this is a mandatory meter replacement/upgrade. The Tulsa Water & Sewer Department requires that all utility customers participate in the program.
What will happen to my old water meter?
Your old meter will be taken by the installation contractor and returned to the City of Tulsa.
Has this new AMR equipment been tested for accuracy and reliability?
AMR meters have been used by utilities throughout the country for decades. All AMR meters used in our system must meet or exceed the AWWA C715 standard for meter accuracy. Each meter shipment is accompanied by factory test data showing the accuracy of the meters.
Will installation of AMR meters cause human meter readers to lose their jobs?
This new system will increase overall efficiency and use of City employees, with one employee able to remotely collect data for many more meters daily. Some positions may be reassigned to other duties once wide-scale efficiencies are realized from the meter installations.
Will this AMR technology lay the groundwork for other customer services?
Once the AMR meters are installed, the City plans to establish an Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) network. The AMI network would allow the City to share regularly updated water usage and leak information for individual users via an online customer portal.
What if I have more questions about the AMR implementation?
You can contact the City of Tulsa Water Department by emailing [email protected] or calling 311.
What is a water service line and how is that different from a water main?
A service line is the section of pipe that connects the home to the water system. These are typically small (<2in. diameter) and connect to the large mainline that runs down residential streets. The service lines are owned by the City of Tulsa up to the water meter, then owned by the customer from the meter to the home.
Are there any health risks with lead water lines?
Lead is a toxic metal that can cause immediate health effects at high doses and long-term health effects if it builds up in the body over many years, even at low levels. While lead is almost never present when water flows from the treatment facility or in water mains, in some older homes lead may be present in the service line or in home plumbing fixtures. There is no safe level of lead, so wherever possible steps should be taken to reduce or eliminate your household’s exposure.
What does the City of Tulsa do to ensure its water is safe?
In order to prevent lead from dissolving into water from lead service lines or home plumbing, the City of Tulsa adjusts the water’s chemistry at the treatment plant. This process is known as corrosion control. Water samples are collected at homes considered to be high risk in order to ensure our corrosion control remains effective.
How do I find out if I have lead in my private water lines?
The City of Tulsa offers free lead testing for any utility customer upon request. if you are concerned you may have lead in your drinking water schedule a free test by contacting the City of Tulsa Water & Sewer Department at (918) 591-4384 for instructions.
How is Tulsa using the AMR meter installation program to look for lead lines?
The City of Tulsa is contracting out meter installations for 145,000 residential customers. During the routine meter change-out process, service line material will be visible. This allows the contractor to perform a materials inspection at the same time as the meter change-out with little additional effort. If at any time lead is found, the contractor will immediately notify the City of Tulsa.
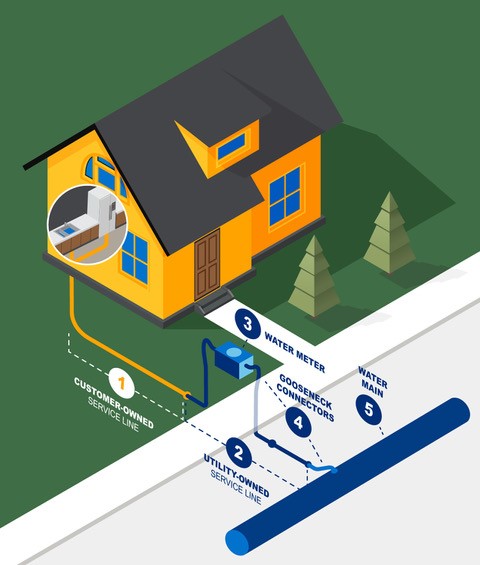
Does Tulsa have an issue with lead in water lines?
Tulsa water mains do not contain lead and historical records show copper and galvanized metal were widely used for service line installations. Occasionally, through routine repairs, maintenance crews have discovered lead connectors in older areas of town. These connectors are small sections of pipe (typically less than 2 ft. long) used to connect a service line to the main or water meter. (See diagram)
Since the 1950s and 1960s, the City of Tulsa has been removing and replacing these lead connectors when they are discovered, but a small number still remain in the system.
What happens if you find a lead line when you’re replacing my water meter?
The contractor is required to immediately notify the City of Tulsa. The Water & Sewer Department will then contact the water user and remove the lead. Staff perform free water quality testing and provide the water user a free water filter to use until results show the water is safe to drink.
How many lead lines/connectors does Tulsa have?
Based on historical records, copper and galvanized metal were widely used for service line installations.
In 2019-2020, approximately 700 homes (built prior to 1950 and at higher risk of lead plumbing) were inspected to find where lead connectors or lead service lines could remain in the system. Lead connectors were found in less than 1% of these higher-risk homes and no lead service lines were found.
Based on these numbers, it is estimated that there are less than 1,000 lead connectors and little, if any, lead service lines remaining in the system.
Where are lead lines/connectors usually found in Tulsa?
Older homes (built prior to 1950) have a higher chance of lead connectors or lead plumbing materials being found. The City of Tulsa has been removing lead in the water system since the 1950s-1960s.
Oklahoma adopted the federal lead ban for plumbing materials in May, 1987, so newer homes built after 1990 should have little risk of being served by a lead service line or lead connector.
The Oklahoma Department of Environmental Quality requires all water suppliers to notify consumers of potential lead service lines. If you have recently received a "Service Line Consumer Notice" letter, more information can be found below.
A full water service line inventory for the City of Tulsa can be viewed HERE. Please note, this is a very large Excel document and it may take several minutes for the entire document to load. Please be patient.
Lead: A dull, silver colored pipe that can be easily scratched with a coin or key. Scratching leaves a shiny silver color. Magnets WILL NOT stick to lead pipes. Lead pipes are bendable and commonly have a "bulb".

Galvanized Iron: A dull, silver colored pipe that is hard to scratch with a coin or key. Scratching leaves a dull gray color. A magnet WILL stick to a galvanized iron pipe.

Copper: Brown colored pipe that can be easily scratched with a coin or key. Scratching leaves a copper color. Magnets WILL NOT stick to copper pipes.

Plastic: Generally, white, black, or blue piping. Plastic piping is rigid. A magnet WILL NOT stick to plastic pipe.

For more information, visit the EPA Lead in Drinking Water Guidance: https://www.epa.gov/ground‐water‐and‐ drinking‐water/basic‐information‐about‐lead‐drinking‐water